



Salesforce-MuleSoft-Developer Exam Questions With Explanations
The best Salesforce-MuleSoft-Developer practice exam questions with research based explanations of each question will help you Prepare & Pass the exam!



Over 15K Students have given a five star review to SalesforceKing



Why choose our Practice Test
By familiarizing yourself with the Salesforce-MuleSoft-Developer exam format and question types, you can reduce test-day anxiety and improve your overall performance.
Up-to-date Content
Ensure you're studying with the latest exam objectives and content.
Unlimited Retakes
We offer unlimited retakes, ensuring you'll prepare each questions properly.
Realistic Exam Questions
Experience exam-like questions designed to mirror the actual Salesforce-MuleSoft-Developer test.
Targeted Learning
Detailed explanations help you understand the reasoning behind correct and incorrect answers.
Increased Confidence
The more you practice, the more confident you will become in your knowledge to pass the exam.
Study whenever you want, from any place in the world.

Salesforce Salesforce-MuleSoft-Developer Exam Sample Questions 2025
Start practicing today and take the fast track to becoming Salesforce Salesforce-MuleSoft-Developer certified.
22344 already prepared
Salesforce Spring 25 Release234 Questions
4.9/5.0

Prep Smart, Pass Easy Your Success Starts Here!
Transform Your Test Prep with Realistic Salesforce-MuleSoft-Developer Exam Questions That Build Confidence and Drive Success!

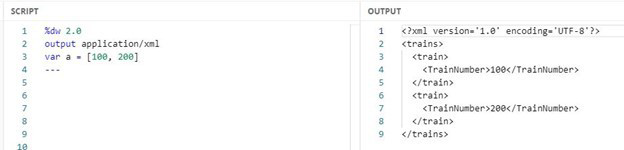
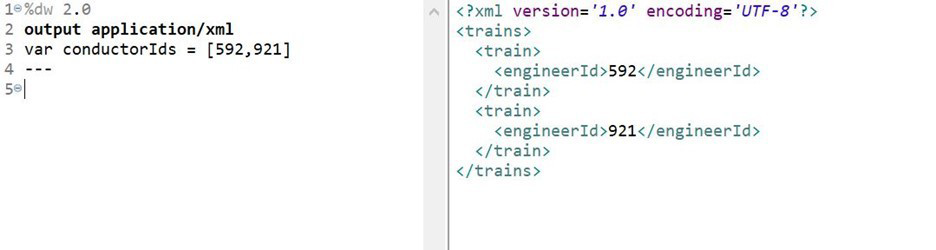 What DataWeave expression transforms the conductorIds array to the XML output?
What DataWeave expression transforms the conductorIds array to the XML output? 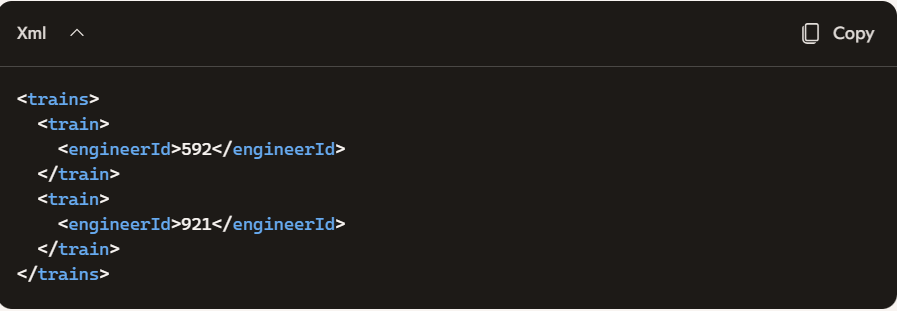 Let’s break it down:
Let’s break it down: