Salesforce-B2C-Commerce-Cloud-Developer Practice Test
Updated On 1-Jan-2026
202 Questions
A merchant has complained to the developers that some products are not appearing in the
storefront and has asked them to diagnose and solve the issue.
Which two factors might be causing a product to be hidden?
Choose 2 answers
A. Product has been set to searchable.
B. Product lacks a price.
C. Product does not have any images.
D. ProductAvailable to sell is <1.
E. Product is not online.
E. Product is not online.
Explanation:
In Salesforce B2C Commerce (SFCC), several conditions must be met for a product to appear in the storefront (search results, category listings, PDPs, etc.). If a product is missing, these are commonly overlooked reasons.
✅ D. Product Available to sell is <1
✔️ Correct
If ATS (Available To Sell) = 0 (or < 1), and the site is configured to hide out-of-stock products, the product won’t show.
This is managed via inventory settings and may vary per site or per configuration in:
Business Manager → Merchant Tools → Inventory
Or via storefront logic (SFRA)
➡️ Solution: Increase inventory or allow backorders/display out-of-stock products.
✅E. Product is not online
✔️ Correct
If the product is not marked as Online, it will not be visible in the storefront at all.
This setting is found under:
Business Manager → Merchant Tools → Products and Catalogs → Products
Then toggle the "Online" checkbox.
➡️ Solution: Set the product status to online.
❌ Why the Other Options Are Incorrect:
A. Product has been set to searchable ❌
Being searchable helps products appear in search results, but it does not hide products if they are set as searchable.
A product that is searchable can still be unavailable if other key visibility rules are not met (e.g., not online, out of stock).
B. Product lacks a price ❌
In SFRA, a product without a price can still be shown, though some functionality (like Add to Cart) might be restricted.
Some storefronts display “Call for price” or hide the price instead — but the product still shows up.
C. Product does not have any images ❌
A missing image does not prevent the product from showing in the storefront.
It might look incomplete or unappealing, but it will still appear unless explicitly filtered out via custom logic.
Adeveloper cannot create a custom object in Business Manager because the attributes do
not show. The developer can view the object but not the attributes.
Which action should the developer take to resolve the problem?
A. Change the data type of the attributes.
B. Create an attribute Group with the desired attributes in it.
C. Set the attributes to site-specific replicable.
Explanation:
Key Issue:
The developer can view the custom object in Business Manager but cannot see its attributes.
This typically happens when attributes are not assigned to an attribute group.
Why Option B?
✅ Attribute Groups Are Required for Visibility
In Salesforce B2C Commerce, attributes must belong to an attribute group to be visible in Business Manager.
Steps to resolve:
Go to Merchant Tools > Products & Catalogs > Attribute Groups.
Create a new Attribute Group (or use an existing one).
Add the missing attributes to the group.
Result: The attributes will now appear in the custom object’s UI.
Why Not Other Options?
❌ A. Change the data type
This won’t fix visibility issues if the attribute isn’t in a group.
❌ C. Set attributes as site-specific replicable
This controls multi-site replication, not visibility in Business Manager.
Reference:
Salesforce Docs: Attribute Groups
Best Practice: Always assign attributes to groups for proper management.
A developer is asked to implementa simple call to an authentication - protected REST web
service.
Which configuration is valid?
A. Add the authentication password to the service credentials
B. Configure the authentication username using a site preference
C. Insert the service'sendpoint in a .properties file
Explanation:
Secure Configuration for Authenticated Web Services
When implementing an authenticated REST web service call in Salesforce B2C Commerce, the Service Framework relies on service credentials to manage sensitive data like usernames, passwords, tokens, and authentication headers.
✅ Option A: Add the authentication password to the service credentials
Correct and secure
In Business Manager, under:
Administration > Operations > Services > Credentials
the developer configures:
Username
Password
Additional headers or tokens if needed
These credentials are linked to a service profile, which is then tied to the actual service.
Avoids hardcoding sensitive data in scripts or templates.
📌 This method ensures separation of concerns and keeps authentication flexible across environments (sandbox, staging, production).
❌ Option B: Configure authentication username using a site preference
Incorrect
Site preferences are meant for site-specific business settings, not authentication for external services.
Storing credentials here is not secure, not encrypted, and not intended for use in service logic.
❌ Option C: Insert the service’s endpoint in a .properties file
Partially relevant, but not the right answer for authentication
.properties files can contain endpoint URLs or configuration flags, but:
They’re not suitable for storing credentials
They don't participate in the secure credential flow for service invocations
🔗 Reference:
“Credential information for authentication-protected services must be configured in the Credentials module and linked to the service profile.” — Salesforce B2C Commerce | Service Framework Guide
📖 Service and Credentials Setup
A controller route in the SFRA base looks as follows:
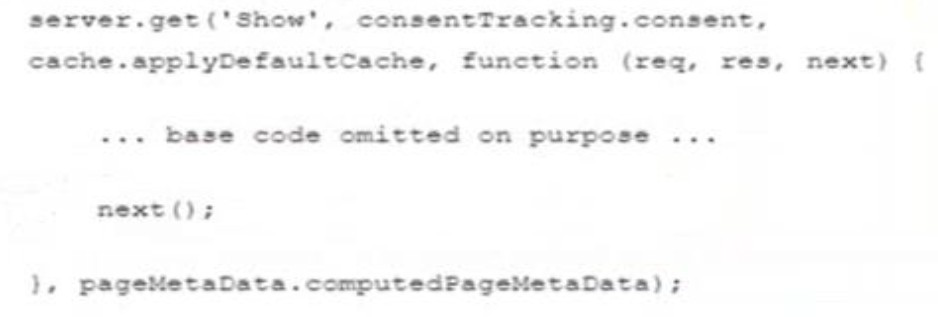
In order to extend this route using prepared ( ), what should the developer consider?
A. Specifyany middleware functions needed for the new functionality.
B. Specify any middleware functions needed for the new functionality using only those called by thebase route.
C. Remove next ( ); on the new route so only the route's middleware functions execute.
Explanation:
The code shown is a controller route definition in SFRA using server.get():
server.get('Show', consentTracking.consent, cache.applyDefaultCache, function (req, res, next) {
// base code ...
next();
}, pageMetaData.computedPageMetaData);
This route uses middleware functions like consentTracking.consent, cache.applyDefaultCache, and pageMetaData.computedPageMetaData.
🔄 When Extending a Route Using server.append() or server.prepend():
You can add custom behavior before or after the base implementation.
Middleware like consentTracking.consent and cache.applyDefaultCache is not automatically inherited — you must explicitly specify any middleware needed for your extension.
The next() call inside the base route enables middleware chaining, so extensions defined with .append() will execute after that.
🧠 What You Must Consider:
When using .append('Show', ...), your custom route function will not inherit any middleware used in the base route. You must explicitly specify any that are needed for your logic to function correctly.
So:
✅ You can add any middleware functions needed — not just those used in the base route.
You are free to add new ones depending on your custom logic.
❌ Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
B. Only use middleware from the base route
❌ Too restrictive. You can use any middleware your logic requires — not just the ones from the base.
C. Remove next()
❌ Removing next() from the base would prevent .append() logic from running. It must be retained to allow proper chaining.
A developer configures the dw.json file and needs to fill in the necessary parameters to
complete the task.
Which threeparameters are required when using npm scripts?
Choose 3 answers
A. Usemame/Password
B. Code Version
C. Hostname
D. Site ID
E. CSRF Token
C. Hostname
D. Site ID
Explanation:
When configuring the dw.json file for use with npm scripts in Salesforce B2C Commerce, the required parameters are B. Code Version, C. Hostname, and D. Site ID. These settings enable the npm scripts (e.g., upload, deploy) to connect to the correct instance, target the appropriate site, and use the specified code version for deployment or other operations.
Reasoning:
dw.json Configuration: The dw.json file is used by the B2C Commerce CLI (via npm scripts) to define connection and deployment settings for interacting with a sandbox or instance.
Required Parameters:
B. Code Version: Specifies the code version (e.g., version1) to deploy or activate. This is mandatory to ensure the correct codebase is used during operations like npm run deploy.
C. Hostname: Defines the instance hostname (e.g., dev01-001.demandware.net) to connect to the B2C Commerce environment. This is essential for establishing the API connection.
D. Site ID: Identifies the target site (e.g., RefArch or SiteGenesis) for the operation. This is required to scope the deployment or action to the correct site.
Example dw.json:
{
"hostname": "dev01-001.demandware.net",
"code-version": "version1",
"site-id": "RefArch",
"username": "admin",
"password": "password"
}
Optional Parameters:
A. Username/Password: These are used for authentication but are not always required if credentials are managed separately (e.g., via environment variables or a credentials file). They are optional in dw.json if other authentication methods are configured.
E. CSRF Token: This is not a parameter in dw.json; it’s an internal security token used during API requests but handled automatically by the CLI, not manually specified.
Reference:
Salesforce B2C Commerce Documentation: CLI Configuration lists required and optional dw.json parameters.
Trailhead Module: “B2C Commerce Developer” module on “Development Tools” covers npm script setup.
Exam Tip:
For the Salesforce B2C-Commerce-Developer exam, know that dw.json requires hostname, code-version, and site-id for npm script operations. Be cautious of distractors like CSRF Token (not configurable) or Username/Password (optional).
| Salesforce-B2C-Commerce-Cloud-Developer Exam Questions - Home | Previous |
| Page 6 out of 41 Pages |