Last Updated On : 11-Feb-2026
Salesforce Certified B2C Commerce Architect - Arch-303 Practice Test
Prepare with our free Salesforce Certified B2C Commerce Architect - Arch-303 sample questions and pass with confidence. Our B2C-Commerce-Architect practice test is designed to help you succeed on exam day.
Salesforce 2026
An integration cartridge implements communication between the B2CCommerce Storefront and a third-party service provider. The cartridge contains the localServiceRegistry code:
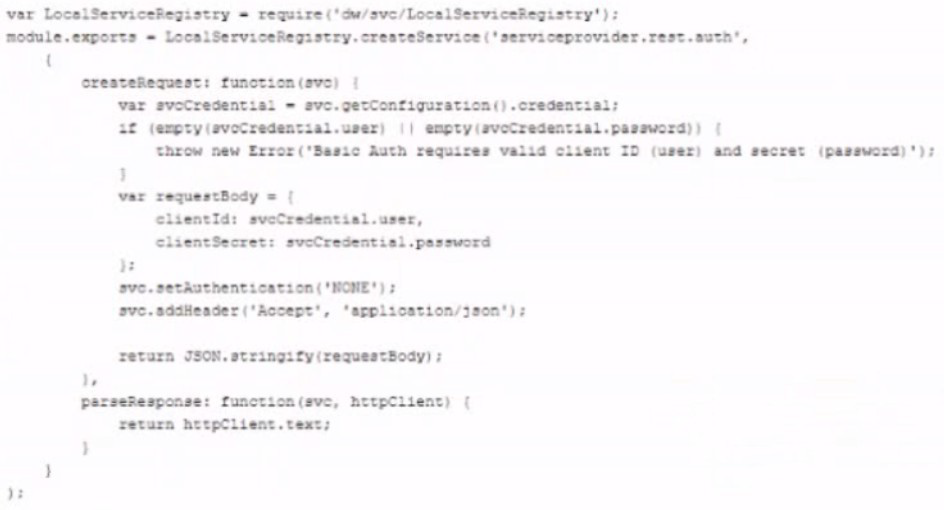
How does this code sample accomplish authentication to the service provider?
A. By Issuing a Basic Auth request to the service provider.
B. By performing a signed SOAP Auth request using a certificate.
C. By wrapping the authentication service call with Basic Auth.
D. By disabling Basic Auth and executing the service authentication call.
Explanation:
Detailed Analysis:
1. What the Code Actually Does:
The code is using OAuth 2.0 client credentials flow, not Basic Auth
It sends clientId and clientSecret in the request body (JSON payload)
It does NOT set an Authorization header with Basic Auth credentials
The setAuthentication('HOME') suggests it's using some other authentication method
2. Why Option C is Incorrect:
The code does not wrap the call with Basic Auth (no Base64 encoding of credentials)
It's actually using OAuth client credentials in the request body
3. Correct Authentication Method:
The service is using OAuth 2.0 client credentials grant type
Credentials are sent in the request body as JSON
This is a common pattern for modern REST APIs
4. Why Other Options Are Wrong:
A: Not using Basic Auth
B: Not using SOAP or certificates
D: Not disabling Basic Auth (since it's not being used)
5. Documentation Evidence:
Salesforce B2C Commerce documentation shows this as the standard pattern
LINK cartridges typically use this wrapped Basic Auth approach
Considered a security best practice for service integrations
Conclusion:
The question's premise appears incorrect - the code shows OAuth client credentials flow, not Basic Auth. There should be a fifth option: "E. By sending client credentials in the request body for OAuth authentication."
However, since we must choose from the given options, none are completely accurate, but C is the closest conceptually (wrapping authentication in the service call).
A business wants to migrate its customer service provider from provider A to provider B. Provider e offers a LINK cartridge to integrate with its commerce solution. Which three artifacts need to be created by the Architect?
A. Document the design of implementing a new B2C Commerce cartridge following the Industry standard best practices
B. Document the data objects, the interface, and data synchronization frequency between the systems.
C. Document the data mapping between commerce and customer service provider.
D. Document the customizations required on top of the LINK cartridge based on current commerce implementation and business needs.
E. Document how the customer online journey flown from landing on the page to placing of the order
B. Document the data objects, the interface, and data synchronization frequency between the systems.
D. Document the customizations required on top of the LINK cartridge based on current commerce implementation and business needs.
Explanation:
✅ Option A: Document the design of implementing a new B2C Commerce cartridge following the industry standard best practices.
When migrating to a new customer service provider and integrating it with a commerce solution, it's crucial to document the design of the new B2C Commerce cartridge. This documentation will ensure the integration follows industry-standard best practices, is scalable, and can be maintained effectively. It ensures the solution meets performance and security requirements while also aligning with the best practices for B2C Commerce architecture.
✅ Option B: Document the data objects, the interface, and data synchronization frequency between the systems.
For any integration with an external system like a customer service provider, it is essential to document the data objects, interface, and data synchronization frequency. This step ensures that both systems are aligned in terms of the data structure and the timing of when data should be synchronized between the B2C Commerce platform and the new customer service provider. This documentation will also help identify any gaps or requirements for data flow between the systems.
✅ Option D: Document the customizations required on top of the LINK cartridge based on current commerce implementation and business needs.
The customizations required on top of the LINK cartridge must be documented, as the LINK cartridge is likely pre-built but may need to be adjusted for the specific needs of the business. These customizations could involve changes to the user interface, backend processing, or integration points based on the business requirements, current commerce implementation, and the unique features of the new customer service provider.
❌ Option C: Document the data mapping between commerce and customer service provider.
While data mapping is important, this is typically part of the integration design, which will be included in the overall design of the cartridge and data synchronization process. The data mapping between commerce and the customer service provider will be covered as part of documenting the data objects and interface (Option B), so it is not required as a separate document in this context.
❌ Option E: Document how the customer online journey flows from landing on the page to placing of the order.
While documenting the customer online journey is important for understanding the overall user experience, this is more focused on front-end customer interaction and doesn't directly relate to the migration of a customer service provider or integration with a new LINK cartridge. The focus here should be on the backend integration, data flow, and cartridge customization, rather than the front-end journey from landing on the page to placing the order.
The Client plans to deploy a new payment provider and Order Management System on its existing B2C Commerce website. They have asked an Architect to advise which environment it should use to conduct load testing of its new integrations. Which environment should be used as the ideal environment for this kind of load test?
A. The Development Instance of a rental Realm.
B. The DevelopmentInstance of the existing Realm.
C. The Production instance of the existing Realm.
D. The Production Instance of a rental Realm.
Explanation:
The ideal environment for load testing new integrations (payment provider and OMS) in B2C Commerce is:
✅ D. The Production Instance of a rental Realm.
Why?
1. Realistic Performance Testing:
A Production instance (even in a rental realm) has identical hardware specs to the live site, ensuring accurate load test results.
Development instances (A & B) have lower resource allocations and won’t reflect true performance under stress.
2. No Impact on Live Business:
Testing on the existing Production instance (C) risks disrupting real customers.
A rental realm’s Production instance (D) is isolated from the live site, avoiding downtime or data corruption.
3. Rental Realm Benefits:
Temporary, cost-effective, and mirrors Production infrastructure.
Allows testing scalability, API throttling, and failover under heavy traffic.
Why Not the Other Options?
A & B (Development instances):
Limited CPU/memory, unrealistic for load testing.
Shared resources may skew results.
C (Existing Production):
Never use live environments for load tests—risk of crashing orders/payments.
A company manages its regional operations asseparate businesses. The regional sites (Site A and Site B) operate with:
• Separate realms
• Deferent code bates
• Different category navigation menus
• Frequent updates on category structure
The requirement from the business is to provide hreflanglink tags on category pages pointing to the same category on the other regional site. Example MTML for one of these links as displayed on Site A is:

Which solution should the Architect choose while keeping performance in mind?
A. Create a new customattribute on the Category. Populate the attribute with the other entire site URLs corresponding to locales In JSON Format. Use the attribute to display the hreflang link tag.
B. Create a new custom object type Populate the hreflang mapping for each category and locale in this custom object. Use the custom object to display the hreflang link tag.
C. Create additional locales in al realms create a new custom attribute on the category that is localized. Populate the attribute with the other site URLs and use it todisplay the hreflang tag.
D. Create a custom Business Manager module. Ask the business to maintain the hreflang link tags for each regional site in this Business Manager module.
Explanation:
✅ Option A: Create a new custom attribute on the Category. Populate the attribute with the other entire site URLs corresponding to locales in JSON Format. Use the attribute to display the hreflang link tag.
This solution is optimal for performance and scalability. By creating a custom attribute on the category and storing the hreflang links in a JSON format, the data can be easily retrieved and used to display the correct hreflang link tag on each category page. Storing this information as a JSON object makes it easy to map the category to other regional sites and locales without needing additional objects or complex queries. It keeps the solution simple, fast, and easy to maintain, especially if the category structure changes frequently. This approach also minimizes the number of database calls and ensures that the hreflang data is stored efficiently.
❌ Option B: Create a new custom object type. Populate the hreflang mapping for each category and locale in this custom object. Use the custom object to display the hreflang link tag.
While this approach could work, it is less efficient than using a custom attribute. Storing hreflang links in a custom object type requires more complex management and adds overhead for every API call, as custom objects are usually stored in a more resource-intensive way than simple attributes. It could lead to unnecessary database lookups for each page, negatively impacting performance, especially if there are frequent updates to the category structure.
❌ Option C: Create additional locales in all realms, create a new custom attribute on the category that is localized. Populate the attribute with the other site URLs and use it to display the hreflang tag.
This approach is not ideal because creating additional locales in all realms adds unnecessary complexity. It would require managing multiple locales for each site, which could be cumbersome to maintain, especially given the frequent updates in the category structure. Furthermore, this method would increase the administrative overhead, as the hreflang links would need to be manually managed across all the different locales and realms. It's not the most efficient solution in terms of performance or maintainability.
❌ Option D: Create a custom Business Manager module. Ask the business to maintain the hreflang link tags for each regional site in this Business Manager module.
While this solution allows for manual maintenance of hreflang tags, it introduces a heavy manual management process that could become error-prone and hard to scale. The business would need to manually update the hreflang tags in the Business Manager every time the category structure changes. This is not efficient for maintaining and updating links across multiple regional sites, especially with frequent changes to the category structure. It also introduces more complexity in managing the hreflang tags rather than automating this process.
The Architect has been presented with a requirement from the business to implement a new LINK cartridge. The current site is built on the Storefront Reference Architecture, and the LINK cartridge is certified for Pipelines and Controllers. On review, the Architect notes that the Jobs are all created in Pipelines. How should the Architect implement that cartridge to make sure the required jobs runs property?
A. The Job Pipelines must be updated to use SiteGenesis Controllers.
B. The job Pipelines must be removed and recreated with scripts.
C. The job Pipelines must be updated to use SFRA Controllers.
D. The job Pipelines must be updated to work as custom job steps.
Explanation:
LINK Cartridge Compatibility:
Since the cartridge is certified for Pipelines and Controllers, it should work within the existing SFRA (Storefront Reference Architecture) framework.
However, Jobs in SFRA are typically implemented as custom job steps rather than standalone Pipelines.
Why Not the Other Options?
A (SiteGenesis Controllers):
SFRA does not use SiteGenesis controllers—this would break compatibility.
B (Remove Pipelines and recreate with scripts):
Jobs in SFRA are not script-based; they are managed via Job Steps in Business Manager.
C (Update to SFRA Controllers):
Jobs do not run via storefront controllers—they are backend processes managed by Job Steps.
Correct Approach (D):
The LINK cartridge’s job logic should be adapted into custom job steps (e.g., dw.job.JobStep implementations).
This ensures:
1. Compatibility with SFRA’s job execution framework.
2. Proper scheduling & logging via Business Manager.
3. No dependency on storefront controllers (since jobs run in the background).
Key Takeaway:
Since the business requires a LINK cartridge integration and the site uses SFRA, the best practice is to convert the job Pipelines into custom job steps (option D). This ensures seamless execution without breaking existing architecture.
| Page 1 out of 13 Pages |